In 2012 I wrote an article called What Ship Is That? which listed a group of programs for tracking ships worldwide. Why would one want to do that? For myself I like to keep track of what ships are sailing on my home coast (the Philippines right now) or for that matter, on the British Columbia coast (my old workplace). It is interesting and informative to anyone that lives on or by the sea. The following story came in from CBC News:
Canadian firm tracks Earth’s ships from space
Data mining with tiny satellites offers new business opportunities
By Emily Chung, CBC News Posted: Aug 12, 2013 5:33 AM ET Last Updated: Aug 12, 2013 12:59 PM ET

ExactEarth’s data allows authorities to monitor whether ships are following maritime traffic laws or straying into protected areas. For example, it could have provided visual data on the Panamanian-registered ship MV Double Prosperity, which ran aground and destroyed a large portion of a marine sanctuary in Sarangani Bay in 2011. (Sarangani Information Office, Cocy Sexcion/Associated Press)
More information here.
[private]
Want to know the location of every freighter and cruise ship plying the Earth’s oceans? That data isn’t easy to get, but a Canadian company can sell it to you, thanks to its view of the Earth from space.
Since 2010, Cambridge, Ont.-based exactEarth Ltd. has been “mining” data about shipping traffic on Earth using satellites — a technique that could potentially be used to collect other, new kinds of valuable data.
‘The ultimate goal is to build out a cluster of businesses around this platform.’—Glenn Smith, Communitech
“Until we started doing this…you had little bits of information, but you really didn’t have a complete domain awareness of what’s out there,” said Philip Miller, the company’s vice president of engineering and operations.
“Once a ship leaves the shore, essentially they’re a sovereign entity …. A captain can go where he wants. And from shore you didn’t know what was happening unless you contacted the ship and asked — whereas now we’re watching, and we know where they go.”
100,000 ships per day
ExactEarth sells information about the more than 100,000 ships it detects per day to over 50 customers on five continents, including ports, navies and governments.
The data can be used for a wide variety of applications, such as:
- Identifying and tracking ship traffic through specific areas, such as the Arctic routes that are opening up as the sea ice melts
- Monitoring whether ships are following maritime traffic laws or straying into protected areas
- Detecting illegal fishing and piracy, or coordinating search-and-rescue operations during natural disasters.
Last year, the company doubled its customer base, doubled its revenues from $4.8 million to $9.6 million and had total order bookings of about $13.6 million, according to the 2012 financial report from its parent company, COM Dev, a satellite equipment maker that trades publicly on the Toronto Stock Exchange.
COM Dev predicted that by the end of 2013, exactEarth would become “a positive contributor to our cash flow.”
Not designed for detection from space
ExactEarth gets its marketable data by detecting over five million messages a day from automatic identification system (AIS) signals that passenger ships and ships over 300 tonnes (Class A vessels) are required to send out under international law.
The VHF radio signals, mandated by the International Maritime Authority since 2002 to reduce the risk of collisions, provide information about a vessel’s course, speed, position, size, destination and identification to nearby ships and monitoring and navigation stations. ExactEarth can also detect signals from some smaller vessels that use a lower-powered version of AIS.
 ExactEarth detects five million messages a day from more than 100,000 ships around the world. (exactEarth)
ExactEarth detects five million messages a day from more than 100,000 ships around the world. (exactEarth)
AIS was designed for close-range communication and not for detection from space, Miller said.
But such detection was plausible — satellites have the ultimate bird’s eye view of Earth, without the obstructions that get in the way on the surface. Our eyes can spot thousands of car headlights and streetlights from an airplane, but with the right detectors, satellites in space can scan a wide area as they orbit and detect signals that have relatively short ranges on Earth.
Miller said ExactEarth started at a time when smaller satellites — suitcase-sized or smaller as opposed to car- or bus-sized — were starting to become more available and affordable. COM Dev began looking for things that it might be able to detect from space with such satellites, beyond traditional environmental monitoring and imaging.
In collaboration with the University of Toronto’s Institute for Aerospace Studies Space Flight Laboratory, the company launched a satellite in 2008 to prove it could detect AIS from space.
 Glenn Smith of Communitech and Robert Zee of UTIAS Space Flight Laboratory hold a life-sized replica of a nanosatellite like one they will be launching in collaboration with exactEarth next year to provide more timely information about ships near the equator. (Emily Chung/CBC)
Glenn Smith of Communitech and Robert Zee of UTIAS Space Flight Laboratory hold a life-sized replica of a nanosatellite like one they will be launching in collaboration with exactEarth next year to provide more timely information about ships near the equator. (Emily Chung/CBC)
ExactEarth began commercial service in 2010, using satellite technology from other suppliers. It launched two additional satellites of its own in 2011 and 2012.
ExactEarth’s satellites aren’t the only AIS detectors in space — Rochelle Park, N.J.-based Orbcomm sells data subscriptions similar to ExactEarth’s and already has AIS satellites in both equatorial and polar orbit. Norway launched its AISSat-1 in 2010 and the German Aerospace Center DLR’s AISSat is scheduled to blast off on an Indian launcher later this year.
Miller said most AIS satellites process a lot more data on the satellite than exactEarth’s do, making them substantially different.
“By doing the processing on the ground, we cannot only do more processing, but we can also evolve it over time,” he said, adding that it’s difficult to change anything that’s already in space.
New kinds of data to mine
Some organizations are now interested in trying to mine other types of data from space.
 Satellites like those launched by ExactEarth have the ultimate bird’s eye view of Earth, without the obstructions that get in the way on the surface. With the right detectors, they detect signals that have relatively short ranges on Earth, the way our eyes can spot thousands of car headlights and streetlights from an airplane. (ExactEarth)
Satellites like those launched by ExactEarth have the ultimate bird’s eye view of Earth, without the obstructions that get in the way on the surface. With the right detectors, they detect signals that have relatively short ranges on Earth, the way our eyes can spot thousands of car headlights and streetlights from an airplane. (ExactEarth)
For example, DLR is currently testing a satellite that detects aircraft signals called ADS-B, which are somewhat similar to AIS. If it works, it will allow continuous monitoring of aviation routes, including areas without radar stations, such as the poles, where airplanes are currently untrackable from the ground.
In Canada, the Waterloo Region’s startup incubator Communitech is collaborating with exactEarth and UTIAS on a project called Data.base, which aims to use exactEarth’s expertise to expand Canada’s “data mining from space” industry.
In 2012, the collaboration received $6.4 million from the federal government to:
- Research new applications and markets for the technology that exactEarth has developed to collect, package and view satellite data;
- Work with other businesses that might be interested in getting into the area;
- Improve the satellite technology; and
- Design and develop new software.
“The ultimate goal is to build out a cluster of businesses around this platform,” said Glenn Smith, director of digital media projects management at Communitech.
Data.base thinks that AIS technology can be used outside the shipping agency to track other things. The technology to transfer data between Earth and space securely may be useful to industries such as finance, to transfer sensitive data from place to place on Earth via a satellite in space.
Smith said the group has already had discussions with a number of businesses and “there’s definitely a lot of interest.”
For its part of the collaboration, UTIAS is developing a new 15-kilogram microsatellite with a beefed-up power system that will produce and transmit more data more quickly, for both exactEarth and other companies doing similar work, said Robert Zee, managing director of the space flight lab.
Upcoming nanosatellite launch
Meanwhile, exactEarth wants to improve its detection of the weaker AIS signals of Class B ships and its ability to scan ships near the equator more frequently.
Currently, the company’s satellites are in polar orbit — in the same plane as the north and south poles — and can view only a small part of the equator each time they circle the Earth. That means there are “gaps of multiple hours” where ships near some areas of the equator will not be detected, Miller said.
To address that, exactEarth will launch a new seven-kilogram nanosatellite satellite, built by UTIAS, into orbit around the Earth’s equator. EV-9, which may incorporate some of the new technology that exactEarth is working on with its collaborators, will piggyback into space on the launch of a larger satellite. That launch was originally scheduled for this summer, but is now delayed until early 2014.
The new satellite will allow exactEarth to collect updated data about ships near the equator at least once per hour.
That will allow exactEarth to mine more data more quickly. But as in conventional mining, that’s just the first step.
It’s the refining of the data back on Earth that generates a marketable product that clients will pay for.
“You can collect all this data, and it’s valuable,” Miller said. “But you have to turn it into information and knowledge.”
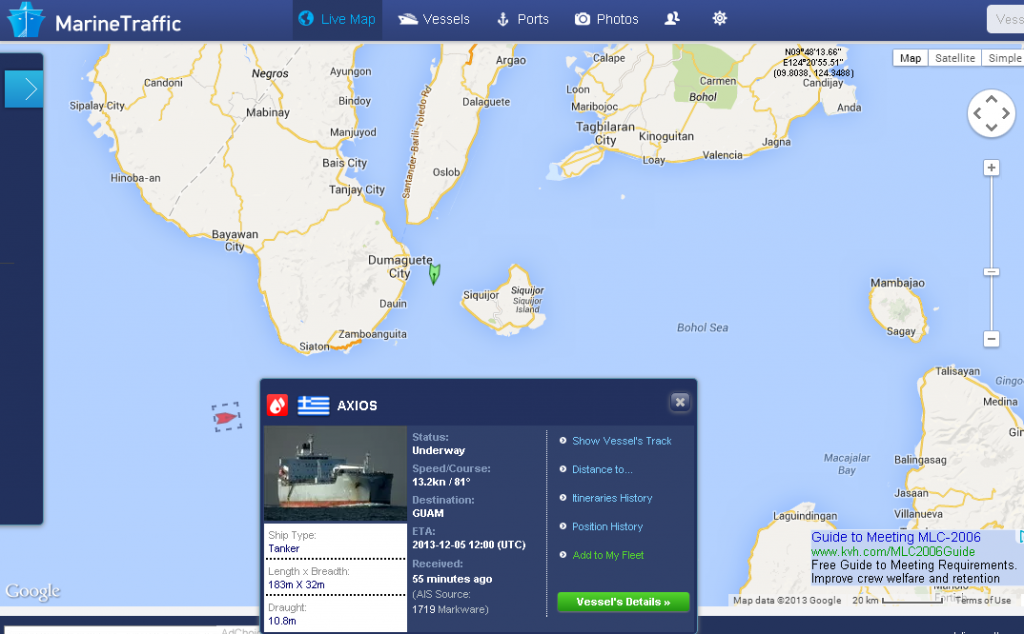
 AIS provides information about a vessels’ course, speed, position, size, destination and identification to nearby ships. ExactEarth can detect the AIS signals from space and use them to track individual ships, as in this data from Sept. 2011. (exactEarth) [/private]
AIS provides information about a vessels’ course, speed, position, size, destination and identification to nearby ships. ExactEarth can detect the AIS signals from space and use them to track individual ships, as in this data from Sept. 2011. (exactEarth) [/private]








 ExactEarth detects five million messages a day from more than 100,000 ships around the world. (exactEarth)
ExactEarth detects five million messages a day from more than 100,000 ships around the world. (exactEarth) Glenn Smith of Communitech and Robert Zee of UTIAS Space Flight Laboratory hold a life-sized replica of a nanosatellite like one they will be launching in collaboration with exactEarth next year to provide more timely information about ships near the equator. (Emily Chung/CBC)
Glenn Smith of Communitech and Robert Zee of UTIAS Space Flight Laboratory hold a life-sized replica of a nanosatellite like one they will be launching in collaboration with exactEarth next year to provide more timely information about ships near the equator. (Emily Chung/CBC) Satellites like those launched by ExactEarth have the ultimate bird’s eye view of Earth, without the obstructions that get in the way on the surface. With the right detectors, they detect signals that have relatively short ranges on Earth, the way our eyes can spot thousands of car headlights and streetlights from an airplane. (ExactEarth)
Satellites like those launched by ExactEarth have the ultimate bird’s eye view of Earth, without the obstructions that get in the way on the surface. With the right detectors, they detect signals that have relatively short ranges on Earth, the way our eyes can spot thousands of car headlights and streetlights from an airplane. (ExactEarth) AIS provides information about a vessels’ course, speed, position, size, destination and identification to nearby ships. ExactEarth can detect the AIS signals from space and use them to track individual ships, as in this data from Sept. 2011. (exactEarth) [/private]
AIS provides information about a vessels’ course, speed, position, size, destination and identification to nearby ships. ExactEarth can detect the AIS signals from space and use them to track individual ships, as in this data from Sept. 2011. (exactEarth) [/private]